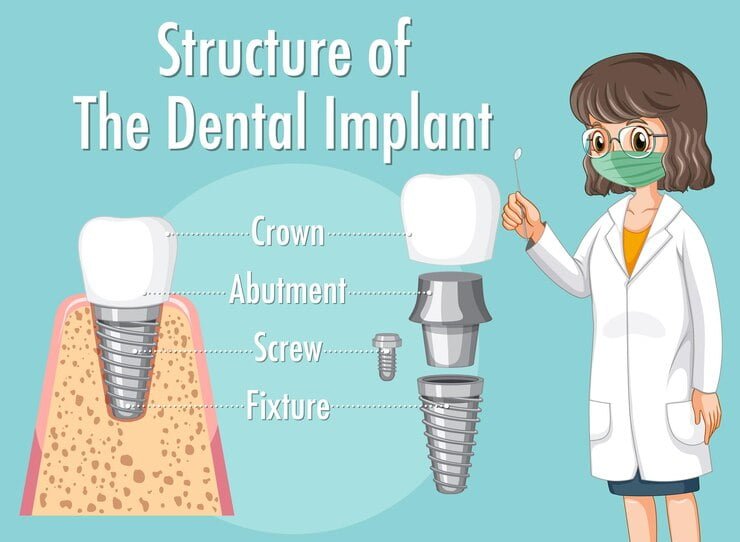
Among the many parts of dental implants which are often overlooked but play an important part is the dental abutment. Knowledge about what a dental abutment is, how it functions and why it is important can help patients and oral health professionals make informed choices. This comprehensive guide will take you through all there is to know about dental abutments including their types and uses as well as the possible frequently asked questions.
What Are Dental Abutments in Real Life?
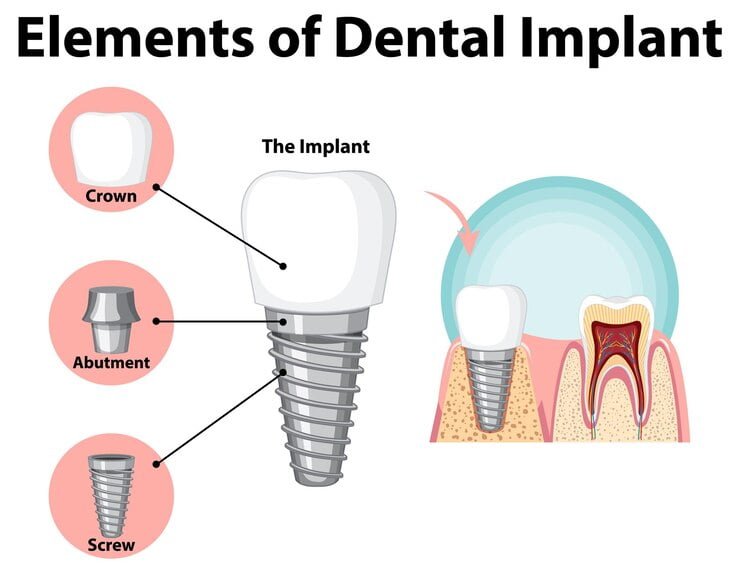
A dental abutment refers to a connector made from titanium, zirconia or gold that fastens a crown, bridge or denture to an implant fixture. The abutment essentially acts like a go-between between the implant and the final prosthetic restoration.
Key Components of a Dental Implant System:
Dental Implant:
A titanium or zirconia post surgically placed into the jawbone that takes on the role of tooth root.
Abutment:
A connector placed above the dental implant.
Crown:
The visible part of this dental rehabilitation that resembles natural teeth.
Types of Dental Abutments
Dental abutments come in various shapes and materials designed for various clinical requirements and patient preferences:
Standard Abutments:
They are prefabricated typically used in simple cases
Custom Abutments:
These are made specifically for individual shapes of gums and implant positions
Angled Abutments:
Placed when an implant was inserted at an angle so as to improve alignment with crown
Temporary Abutments:
Used during healing before placing final restoration
Why Do We Need Dental Abutments?
There are several crucial roles that they play in ensuring success of dental implants:
Stability
This ensures that a prosthesis is securely affixed onto an implant.
Aesthetics
Customized use helps achieve more natural looking gum line.
Functionality
Facilitates proper chewing and speaking by providing a stable foundation for the crown or bridge.
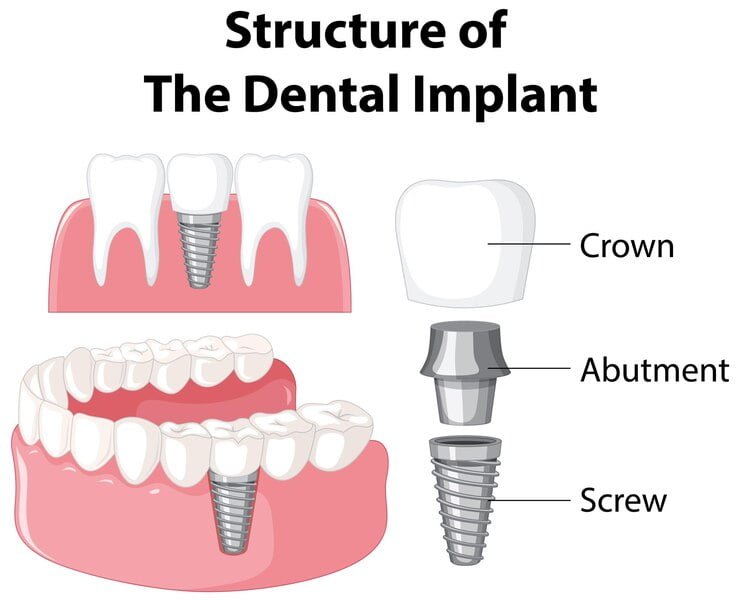
What Is The Procedure Of Placing A Dental Abutment?
The process of placing an abutment usually requires multiple stages, often spread over several months to allow for healing and integration.
Step-by-Step Process:
Implant Placement: It is put through surgery and placed into the bone of the jaw
Healing Period
Implant and bone go through osseointegration, which can last for several months
Abutment Placement
Once osseointegration is complete, the implant is exposed in a minor surgical procedure, and an abutment is attached.
Impression Taking:
Final crown or bridge is fabricated by taking an impression.
Final Restoration:
The dental implant procedure concludes once crown or bridge connects with the abutment.
Materials Used in Dental Abutments
Choice of material for an abutment can have a significant impact on the restoration outcome.
Common Materials:
Titanium
recognized bio-compatibility strength and durability are some advantages associated with titanium
Zirconia
it has tooth color which resembles natural teeth therefore making it look beautiful; besides that it’s also biocompatible.
Gold
although not commonly used but it provides excellent strength as well as being biocompatible.
Selecting Appropriate Material
Material choice typically depends on factors like location of implant, patient preferences, recommendations from dentist among others.
Benefits of Dental Abutments
Understanding the positive sides about dental abutments can help comprehend their significance within dental implantology. Major Benefits:
Enhanced Stability
This results in a strong connection between prosthesis and implant.
Improved Aesthetics
The natural contour of the gums can be replicated using custom abutments.
Longevity
High-quality materials such as titanium and zirconia provide long-lasting results.
Comfort
Properly positioned abutments assure a proper fit, thereby minimizing the chances of experiencing discomfort or acquiring infection.
Issues and Answers
While dental abutments generally perform well, certain issues can arise that require attention.
Potential Issues:
Loosening
Crowns or bridges could be compromised if the abutment becomes loose.
Infection:
Poor hygiene around the abutment may result in gum disease.
Wear and Tear:
With time, it may exhibit signs of deterioration thus necessitating its replacement.
Solutions:
Regular Check-ups: Regular dental visits can help to detect problems at an early stage before they get worse.
Proper Hygiene:
Good oral hygiene helps to prevent infections around the abutment.
Material Choice:
This is because durable materials such as titanium are used hence there is no risk of wear and tear occurrence on the device.
FAQs
What’s the difference between a dental crown and an abutment?
The connector attaching itself to the implant is known as an abutment while on top of it is what we call a crown which are visible part of teeth called crowns (Ishikawa et al., 1995).
How long does it take to place a dental abutment?
Usually, one hour for procedure; implant placement follows this period but healing precedes them all.
Can I have an allergy to a dental abutment?
For example, allergic reactions towards biocompatible substances like titanium or zirconia hardly occur.
How do I care for my dental implant?
Good oral hygiene practices like brushing your teeth twice daily flossing and regular dental checkups are required for the maintenance of dental implant health.
Does getting a dental abutment hurt?
In fact, during the placement procedure, local anesthesia is used; this implies you will not experience any pain . Painkillers sold over-the-counter can help to manage any discomfort that may be present subsequently.
How much does a dental abutment cost?
These prices can go up or down depending on complicity of the case and material employed.
Can an abutment be replaced?
If necessary a dental abutment could be changed, it can bring about wear and tear to that part or even fitting problems.
What are signs of a failing dental implant?
Discomfort, looseness of crown and visible spaces between gum line and crown might indicate the end stage of failure.
Do all implants have an abutment?
Practically all dental implants require an abutment unless they are integrated with crowns as one piece which is rare.
Can I choose the type of abutment I want?
Though you might indicate your preference to your dentist in this regard, he/she will make the ultimate decision based on clinical requirements and their own judgment.
Conclusion
Dental Abutments form a crucial element within Dental Implantology as it is responsible for linking implants with definitive restorations. Appreciating their roles, categories, materials and merits would empower patients, prosthodontists as well as dentistry students towards informed choices in oral care giving.
It is therefore very important for patients considering dental implants, prosthodontists seeking to widen their understandings, and dental students who are eager to know more to have knowledge about dental abutments. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene through regular visits to the dentist and consultations with a dentist so as to get the best results from your dental implant.
Do not hesitate to consult a qualified dentist in case you require further explanations or individual comments. With this information, they will be able offer specific advice that suits the problem at hand.